Bank routing number lookup directory
Make every wire transfer count. Use the right routing number to avoid delays, disruptions, and failed payments.
What is a routing number?
A routing number is a unique nine-digit identifier used in the United States to pinpoint the specific financial institution involved in a transaction. Issued by the American Bankers Association (ABA), this number serves as a critical component of the U.S. banking infrastructure, guiding the accurate transfer of funds between banks.
Think of it as a bank's address—used to direct wire transfers, direct deposits, electronic bill payments, and other automated transactions to the right place. Whether you're receiving a salary, making a payment, or sending money across banks, the routing number ensures each transaction reaches the correct institution without delays or errors.
By helping route payments efficiently and securely, routing numbers play a key role in maintaining the reliability of the banking network.
Why routing numbers matter?
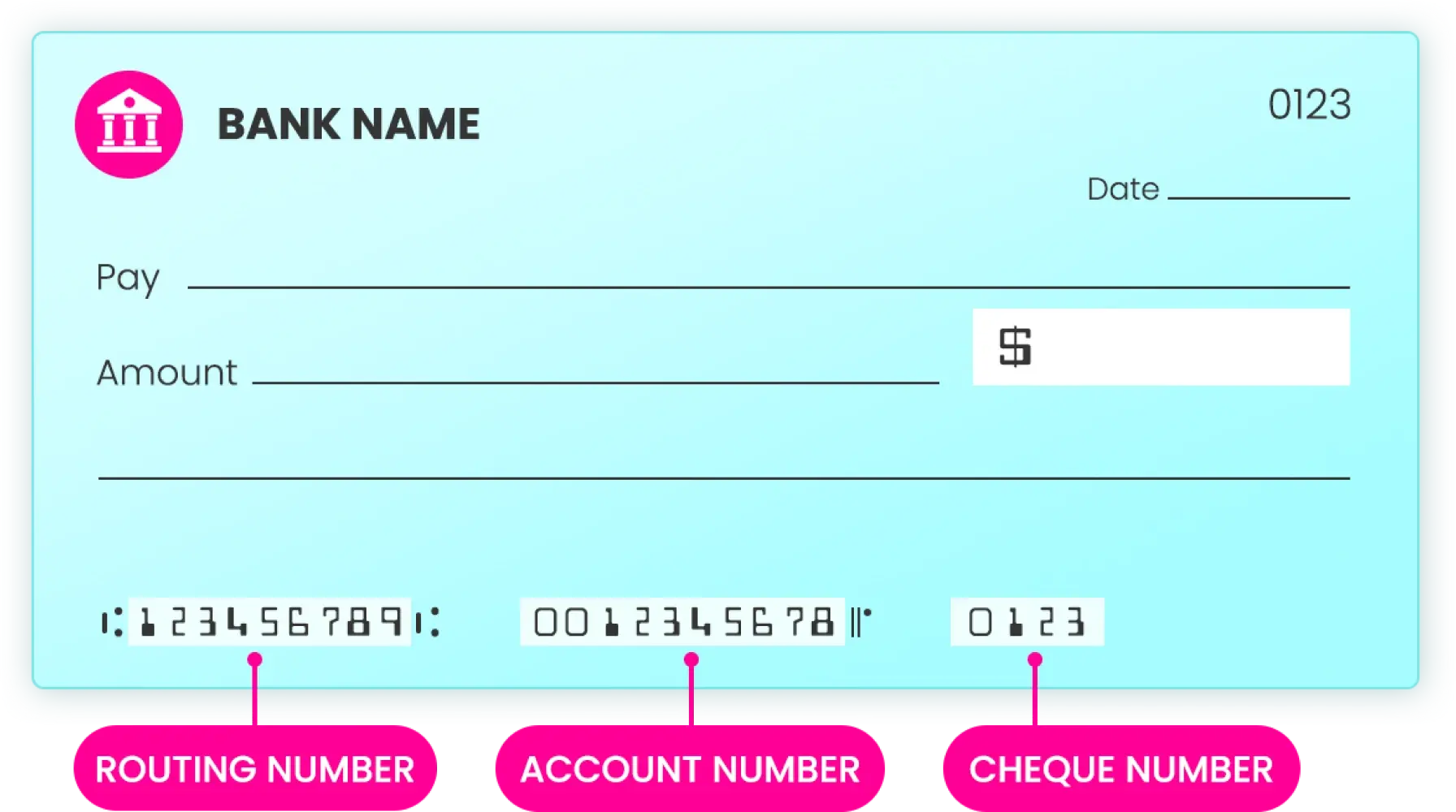
How to find a routing number on a cheque?
To find a routing number on a cheque, look at the bottom-left corner. The first set of nine digits printed on the lower left-hand side of a check is the routing number. This number is followed by the account number and, in some cases, the check number. The routing number is encoded with a magnetic ink character recognition (MICR) font, making it easy for automated systems to read and process.
How to find your routing number online?
There are several easy ways to locate your routing number:
Lookup routing numbers by bank
List of banks
No routing numbers found.
No routing numbers found.